Have you ever been in a quiet room and suddenly noticed the rhythmic sound of your heartbeat in ear? This strange sensation is called pulsatile tinnitus, and it affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the intricacies of this condition and addressing the underlying causes can make a significant difference in managing the symptoms and improving one’s quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- Pulsatile tinnitus affects approximately 1.5 million Americans and is caused by changes in blood flow, often due to vascular issues or ear abnormalities.
- Common causes of pulsatile tinnitus include underlying health conditions such as high blood pressure and anemia, lifestyle factors, infections, malformations in the vessels near the ear & structural abnormalities near the ear.
- Diagnosis & treatment involve a comprehensive medical evaluation including patient history & imaging tests, sound therapy, managing underlying health conditions through medication/lifestyle modifications. Surgical interventions/medications when necessary. Stress management techniques tailored to individual needs
Identifying Pulsatile Tinnitus: Symptoms and Prevalence

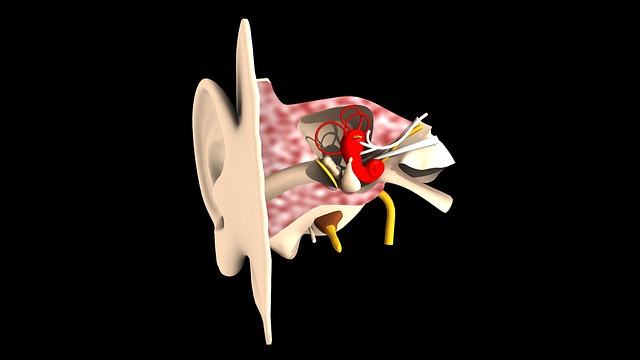
Pulsatile tinnitus is characterized by the constant perception of a regular beat or whooshing sound, often in sync with one’s heartbeat in your ear. It affects approximately 1.5 million Americans and is often more noticeable in quiet environments due to the lack of external noise that would otherwise mask the sound. Pulsatile tinnitus is quite different from regular tinnitus. Many people experience regular tinnitus as a constant ringing or buzzing in their ears.
Symptoms of pulsatile tinnitus include a pulsing or thumping sound, which can affect one or both ears. Those who experience pulsatile tinnitus are dealing with a condition classified as objective tinnitus, meaning that the sound originates from an underlying condition, often related to blood flow or vascular issues. Given that pulsatile tinnitus may signify a severe underlying condition, pursuing an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is of utmost importance.
The Science Behind Pulsatile Tinnitus: Blood Flow and Vascular Issues
The primary cause of pulsatile tinnitus is changes in blood flow, often due to:
- Vascular issues
- Structural abnormalities near the ear
- Alterations in blood flow in nearby blood vessels, such as the arteries and veins in the neck or base of the skull
- Factors such as stenosis in the brain’s large veins or elevated blood pressure can contribute to the development of this condition.
Structural abnormalities affecting the ear, such as the movement of bones inside or near the ear, can also cause pulsatile tinnitus. In some cases, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, a condition characterized by increased pressure inside the skull, may also contribute to the development of this condition.
Common Causes of Pulsatile Tinnitus
The most common causes of pulsatile tinnitus include ear abnormalities, blood vessel disorders, and underlying health conditions such as high blood pressure or anemia.
The proceeding subsections will explore each category in depth, shedding light on the factors that may trigger pulsatile tinnitus.
Ear Abnormalities and Infections
Various ear abnormalities, including those affecting the inner ear, can be associated with pulsatile tinnitus. Sigmoid sinus diverticulum is a medical term. It refers to small pouches protruding through the wall of the sigmoid sinus into the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. Dehiscence, on the other hand, is a lack of a portion of the bone that encloses the sigmoid sinus in the mastoid. These abnormalities may result in the unique sensation of pulsatile tinnitus, hence the need for an exhaustive examination.
Infections affecting the ear can also contribute to pulsatile tinnitus. Conditions such as Meniere’s disease, cholesteatoma, and labyrinthitis can cause a range of symptoms, including dizziness, hearing loss, and tinnitus. Accurate diagnosis and treatment of these infections are vital in symptom relief and prevention of additional complications.
Blood Vessel Disorders and Malformations
Blood vessel disorders and malformations refer to abnormalities in the structure or function of blood vessels, which can result in pulsatile tinnitus. Glomus tumors, for example, are locally invasive growths originating from glomus cells and often located in the jugular vein below the middle ear. Tumors can press on the blood vessels in the head or neck, leading to pulsatile tinnitus and other associated symptoms. This kind of tinnitus is usually caused by a tumor..
Carotid artery dissection, another blood vessel disorder, involves the tearing of the walls of the carotid arteries. Treatment for this condition typically includes anti-clotting medication for a period of 3-6 months and, in some cases, surgery. Attending to these blood vessel disorders and malformations is key to managing pulsatile tinnitus effectively.
Lifestyle Factors and Underlying Health Conditions
Pulsatile tinnitus can also be associated with various underlying health conditions, such as high blood pressure and anemia. Hyperthyroidism and elevated intracranial pressure are other potential underlying health conditions to consider. In some cases, lifestyle factors like strenuous exercise, pregnancy, and issues with heart valves can lead to generalized increased blood flow, resulting in pulsatile tinnitus.
Addressing these underlying health conditions entails:
- Seeking medical attention
- Undergoing necessary medical tests and examinations
- Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medication, or surgical intervention, depending on the specific condition and its severity.
Diagnosing Pulsatile Tinnitus: Tests and Examinations
Diagnosing pulsatile tinnitus involves a thorough medical evaluation, including patient history, physical examination, and imaging tests. A hearing test, audiologic evaluation, angiography, computerized tomographic angiography (CTA), computerized tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), tympanometry, and MRI scans are among the tests employed to diagnose pulsatile tinnitus.
Blood tests and thyroid function tests may also be required to exclude anemia or thyroid issues as potential underlying causes. A proper diagnosis is pivotal in selecting the suitable treatment options and effectively managing the condition.
Effective Treatment Options for Pulsatile Tinnitus
Treatment options for pulsatile tinnitus depend on the underlying cause and may include addressing underlying health conditions, sound therapy, and surgical interventions or medications when necessary.
The upcoming subsections will delve into each treatment strategy in further detail.
Managing Underlying Health Conditions
Addressing various health conditions such as:
- high blood pressure
- brain inflammation
- thyroid disease
- heart disease
- severe anemia
can be an effective treatment for pulsatile tinnitus. Treatment may involve lifestyle modifications, such as minimizing stress and optimizing diet and physical activity, in addition to medication. Properly managing these health conditions can alleviate the symptoms of pulsatile tinnitus and improve one’s overall health.
Working closely with healthcare providers is crucial to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment of the underlying health conditions. This collaborative approach can lead to better outcomes and a more comprehensive understanding of the factors contributing to pulsatile tinnitus.
Sound Therapy and Hearing Aids
Sound therapy is a valuable tool for tinnitus sufferers, particularly those experiencing pulsatile tinnitus. Techniques such as noise-suppressing devices or wearable sound generators can help manage symptoms by masking the pulsatile tinnitus or promoting habituation, making the individual less aware of the noise.
Counseling options such as tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can also be advantageous in managing pulsatile tinnitus. These approaches help individuals develop coping strategies and improve their ability to manage the impact of tinnitus on their daily lives.
Surgical Interventions and Medications
In some cases, surgical interventions or medications may be necessary to treat pulsatile tinnitus. Surgical options include:
- Insertion of a stent in a narrowed vein
- Endovascular coiling/stenting
- Transmastoid surgery
- Intravascular intervention for pulsatile tinnitus associated with sigmoid sinus
- Otological or neurological surgery for identified vascular or osteological sources
- Sigmoid sinus resurfacing
Medications may also play a role in treating pulsatile tinnitus, particularly when the condition is caused by high blood pressure. In such cases, medication in conjunction with lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health.
Tips for Living with Pulsatile Tinnitus
Living with pulsatile tinnitus can be challenging, but implementing certain lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being. Stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness practices, can help individuals cope with the condition and reduce its impact on daily life.
Alongside stress management, utilizing sound therapy techniques like white noise machines or nature sounds can aid in masking the pulsatile tinnitus, making it less perceptible. Individuals must identify their optimal coping mechanisms and exhibit patience, as managing pulsatile tinnitus typically necessitates a blend of strategies, customized to each person’s distinct needs.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Pulsatile Tinnitus
It is necessary to seek medical attention for pulsatile tinnitus if the symptoms persist, worsen, or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as severe headaches or vision changes. Ignoring these symptoms and delaying medical intervention can lead to further complications and a reduced quality of life.
Prompt medical attention and undergoing the required tests and examinations allow individuals to comprehend the underlying causes of their pulsatile tinnitus better. This enables them to collaborate with healthcare professionals in developing an all-encompassing treatment plan. This proactive approach can lead to better outcomes and an improved ability to manage the condition.
Expert Guidance: Audiologists and ENT Specialists
Audiologists and ENT specialists possess expertise in diagnosing and treating hearing and balance disorders, including pulsatile tinnitus. They are capable of providing patient-centered care, evaluating and managing the condition, and offering counseling options such as tinnitus retraining therapy. Closely collaborating with these experts is vital for an accurate diagnosis and treatment of pulsatile tinnitus.
Maintaining a symptom journal can help your audiologist gain a better comprehension of your condition. This collaborative approach allows for a more personalized treatment plan and can significantly improve the overall management of pulsatile tinnitus.
Summary
In summary, pulsatile tinnitus is a complex condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms, underlying causes, and available treatment options is essential for effectively managing the condition. By seeking expert guidance from audiologists and ENT specialists, implementing lifestyle modifications, and exploring various treatment approaches, individuals can take control of their pulsatile tinnitus and live a fuller, healthier life.
Check out our site, Ear To Hear, to learn more about us and our services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean when you hear your heartbeat in your ear?
When you hear your heartbeat in your ear, it is likely a symptom of pulsatile tinnitus and is usually accompanied by a steady beat or whooshing sound that changes in sync with your heart rate.
Why is pulsatile tinnitus a red flag?
Pulsatile tinnitus is a concerning red flag, as it can be a symptom of vascular disease or an underlying health problem such as stroke or blindness. It is important to seek medical advice immediately if experiencing pulsatile tinnitus.
Is hearing my heartbeat in my ear anxiety?
Pulsatile tinnitus, which is characterized by hearing a heartbeat in the ear, is often linked to mental health conditions such as anxiety. Treatment of this condition can reduce the distress caused by the sound. Therefore, hearing a heartbeat in the ear may indicate an anxiety issue.
What is the most common cause of pulsatile tinnitus?
The most common cause of pulsatile tinnitus is disorders or malformations in the blood vessels and arteries, such as venous sinus stenosis/IIH and dural arteriovenous fistula. These abnormalities may require medical attention and treatment to address the underlying causes.
How to stop ears from ringing?
To stop ears from ringing, avoid things that may make it worse such as caffeine, alcohol, and smoking, get enough rest, use sound therapy or maskers, reduce stress, try a Mediterranean diet, and limit alcohol and nicotine while using white noise machines or low-volume radio static to mask the


