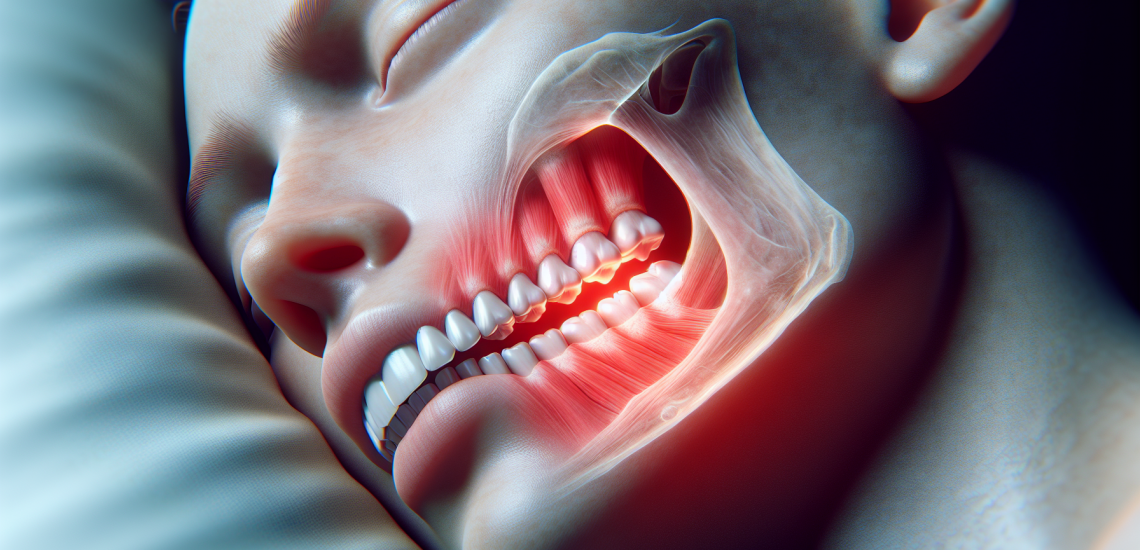
If you’ve ever experienced jaw or ear pain, you’re not alone. These common discomforts can be quite debilitating, affecting daily activities such as eating, speaking, and even sleeping. Despite their prevalence, few understand the intricacies of these conditions and how to effectively address them. This blog post aims to shed light on the common causes of jaw and ear pain and provide useful strategies to alleviate these afflictions, ultimately helping you regain control over your health and quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- TMJ disorders can lead to jaw and ear pain, with treatments ranging from medications to surgery.
- Dental issues such as cavities or abscesses are also linked to jaw and ear pain.
- Severe and persistent discomfort should be evaluated by a medical professional for diagnosis of the underlying cause.
Understanding TMJ Disorders
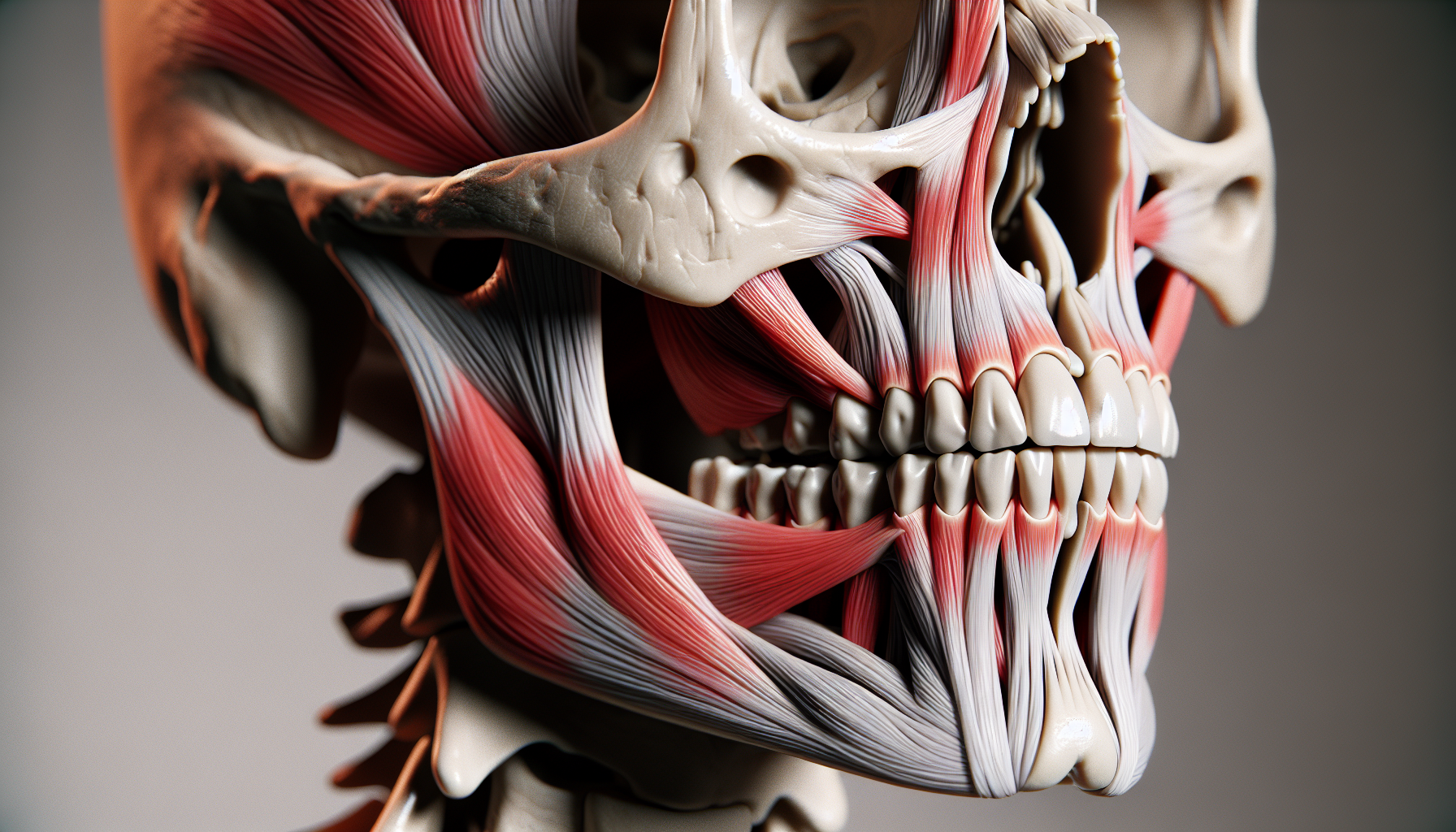
TMJ disorders refer to conditions associated with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), a joint connecting the jaw to the skull, specifically to the temporal bone. When inflamed or affected by wear and tear, this joint can cause discomfort below the ear and behind the jaw bone. Symptoms of TMJ disorders can include:
- Clicking or popping noise in the jaw joint when opening and closing the mouth
- Pain during chewing
- Headaches
- Hearing loss
If you’re experiencing these symptoms persistently for more than three months, you could be suffering from chronic TMJ syndrome. But what causes tmj disorder? Factors contributing to TMJ disorders can be inflammation, wear and tear, or other medical conditions affecting the temporomandibular joint.
Treatments for TMJ disorders vary greatly, from:
- anti-inflammatory medications
- physical therapy
- splints or mouthguards
- counseling or stress management techniques
- surgery (in severe cases)
Consult with a healthcare professional should TMJ pain persist, or if you experience jaw and ear pain in the absence of injuries or other infection signs like fever or runny nose.
Dental Issues and Their Impact on Jaw and Ear Pain
Apart from TMJ disorders, dental issues can also cause significant jaw and ear pain. Problems like cavities, abscesses, and gum inflammation often stem from inadequate oral hygiene or infections, leading to discomfort in your jaw and ear.
Symptoms that could indicate dental issues as the potential cause of your pain include:
- tooth sensitivity
- facial pain
- loose teeth
- sensitivity to hot or cold drinks
- gum swelling
In fact, a tooth abscess can lead to ear and jaw pain as the infection spreads, causing gum swelling and tenderness around the teeth.
As we delve into the other causes of jaw and ear pain, you’ll find that arthritis, often associated with joint pain, is also a contributing factor.
The Connection Between Arthritis and Jaw and Ear Pain
Arthritis, specifically osteoarthritis, impacts the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and can lead to significant discomfort in the jaw and ear, sometimes resulting in temporomandibular joint disorder. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and is characterized by gradual deterioration of the joint’s surrounding cartilage, resulting in stiffness and discomfort in the joint.
The typical indicators of osteoarthritis in the TMJ include pain and stiffness in the joint, potentially leading to significant discomfort behind the ear and jaw, which can be worsened by periodontal disease. But osteoarthritis isn’t the only type of arthritis that can cause these symptoms.
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are autoimmune conditions that can lead to pain in the jaw and ear by causing the immune system to attack healthy joints, including those in the TMJ. The pain caused by these conditions can be exacerbated by specific triggers, which differ from person to person.
Swimmer’s Ear: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Swimmer’s ear, medically known as otitis externa, is a bacterial infection in the outer ear, often caused by exposure to water or injury. This condition can lead to significant discomfort, including jaw and ear pain. When water enters the ear during swimming or bathing, it can remain in the ear canal, creating a moist environment that promotes bacterial growth. Similarly, injury to the lining of the ear can also lead to swimmer’s ear. It is important to note that swimmer’s ear affects the outer ear and not the inner ear.
Ear and jaw pain are major indicators of swimmer’s ear. If you suspect you have this condition, don’t hesitate to seek medical aid to ease the pain and halt the infection from escalating. As diverse as these causes may be, sinusitis is another common factor contributing to jaw and ear pain.
Sinusitis and Its Relation to Jaw and Ear Pain
Sinusitis is characterized as an inflammation of the nasal passages, and it can significantly contribute to jaw and ear pain. This condition is commonly caused by a virus, though bacteria can also play a significant role.
Due to the proximity of the sinuses to the jaw and ear structures, discomfort from a sinus infection can extend to the teeth, jaw, and ears, causing pain. But sinusitis isn’t the only condition that can lead to these symptoms. Another common cause is teeth grinding.
Teeth Grinding: Effects on Jaw and Ear Pain
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, occurs when a person involuntarily grinds or clenches their teeth, often during sleep. This action can exert pressure on the temporomandibular joint and the adjacent muscles, leading to discomfort and pain in the ear and jaw area.
Symptoms commonly associated with teeth grinding that are connected to the jaw and ears include pain in these areas and may also result in headaches. Signs of teeth grinding may include unexplained pain in the jaw or ears, particularly upon waking, which could indicate teeth grinding during sleep.
Persistent teeth grinding may result in jaw disorders, headaches, damaged teeth, and temporomandibular disorders (TMJ Syndrome). This can lead to ongoing discomfort in the head, neck, and ears, as well as earaches and discomfort. However, jaw injuries can also result in these symptoms.
Jaw Injuries and Resulting Pain
Jaw injuries and issues that can cause your jaw hurts, such as:
- broken jaws
- muscle strains or sprains around the jaw
- dislocations
- fractures
- misaligned teeth
- TMJ disorders
- TMJ dysfunction
can all cause significant discomfort in the jaw and ear. The proximity and connection between the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and the ear can explain how a jaw injury can cause ear pain. Injuries to the jaw muscles or TMJ can lead to referred pain in the ear, and factors such as inflammation or dysfunction of the TMJ can contribute to the sensation of ear pain.
Oral trauma is diagnosed through a physical examination, dental X-rays, and sometimes additional imaging tests. The treatment approach is determined by the type and severity of the injury, involving:
- wound cleaning and suturing
- splinting or repositioning of teeth
- root canal treatment
- tooth extraction if deemed necessary
Supportive treatments may include pain management and antibiotics. Although these medical treatments are effective, there are also home remedies that can provide relief.
Home Remedies for Alleviating Jaw and Ear Pain
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil) have been found to effectively reduce pain and inflammation, providing relief from jaw and ear pain.
Apart from medication, warm compresses are beneficial for jaw and ear pain as they help relax the muscles, increase blood flow, and reduce inflammation, providing relief from pain and discomfort. Though these home remedies can offer relief, if pain persists, it’s important to pursue medical treatment options.
Medical Treatments for Persistent Jaw and Ear Pain
Antibiotics such as Amoxicillin, penicillin, azithromycin, clindamycin, cephalexin, and metronidazole, as well as anti-inflammatory medications like NSAIDs, including Naprosyn (naproxen), Feldene (piroxicam), and Mobic (meloxicam) can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. However, these medications should be taken with caution due to potential side effects such as stomach pain, ulcers, headaches, lightheadedness, ringing in the ears, concentration difficulties, and rashes.
Additional therapies are advised for severe instances of jaw and ear pain that do not sufficiently respond to medication. These instances include those arising from TMJ disorders, various types of arthritis like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid, or psoriatic arthritis, as well as migraines, swimmer’s ear, sinusitis, dental issues, and infections. The recommended treatments may involve various options based on the specific condition, such as mouth guards, physical therapy, and surgery, alongside medication and antibiotics.
Physical therapy serves as a vital additional treatment for jaw and ear discomfort, particularly when pain persists. It aims to restore normal jaw functions, alleviate muscle tension, and enhance overall jaw and head movement. Interventions may involve soft tissue mobilization and education on proper postural and body mechanics to prevent future pain episodes.
Surgical interventions for TMJ disorders, while not commonly used, may consist of arthrocentesis, corticosteroid injections, TMJ arthroscopy, and modified condylotomy.
Knowing When to Seek Professional Help
In case of severe, persistent jaw and ear pain, especially if accompanied by other symptoms like high fever, intense pain, swelling, or dizziness, it’s important to promptly seek medical attention. Some severe symptoms that necessitate immediate medical attention include chest pain or pressure that radiates to the jaw or upper back, and shortness of breath.
Additional symptoms that should be taken into consideration as indicators for seeking professional help alongside jaw and ear pain include:
- pain in one or both of the temporomandibular joints
- aching pain in and around the ear
- difficulty chewing or pain while chewing
- aching facial pain
Should jaw and ear pain persist or intensify despite self-management over a short period, seeking professional medical assistance is recommended.
Summary
In conclusion, jaw and ear pain can stem from a variety of conditions, from TMJ disorders and dental issues to arthritis, swimmer’s ear, sinusitis, teeth grinding, and jaw injuries. While home remedies and over-the-counter pain relievers can offer temporary relief, persistent or severe symptoms necessitate professional medical attention. Understanding these causes and their corresponding treatments can empower you to take proactive steps towards relief and recovery, improving your overall health and wellbeing.
Take a look at our site Ear To Hear if you enjoyed this article.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean when your jaw and ear hurts?
Pain in your jaw and ear can indicate a temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJD). This condition can cause inflammation and pain in the TMJ, and is characterized by facial pain and ear discomfort. It affects up to 15 percent of adults, so it is important to seek medical advice if you experience such symptoms.
When should I be worried about jaw pain?
If you experience jaw pain that lasts more than a week, or if the pain is severe, you should seek medical help immediately. Severe jaw pain may indicate a broken or dislocated jaw, or be a symptom of a heart attack.
How do I get TMJ to go away?
To get TMJ to go away, maintain the resting position of your jaw, correct your posture, get a good night’s sleep, use hot or cold compress, reduce stress, exercise your jaw, take notice of bad habits and avoid certain activities and foods. Additionally, avoid overuse of jaw muscles, eat soft foods, do stretches and massages, and apply heat or cold.
Can TMJ come on suddenly?
Yes, TMJ can come on suddenly and be very painful. Symptoms include difficulty eating and speaking, significantly impacting quality of life.
Ear pain when chewing?
Pain in your ear when chewing could be due to dysfunction in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which affects at least 10 million people. It is located next to the temporal bone, which includes the inner ear, and it is susceptible to aches and pains from conditions such as teeth grinding or arthritis. To alleviate the pain, take over-the-counter pain medicine and apply warm compresses to the jaw.